Image Formats Guide for Beginners
Introduction
When working with digital images, you've likely encountered file types like JPEG, PNG, or GIF. But what do they mean? Each image format has unique strengths and use cases. Choosing the right one affects image quality, file size, and compatibility. This guide breaks down the most common formats to help you make informed decisions.
Common Image Formats Overview
Here’s a visual overview of the five most widely used image formats:

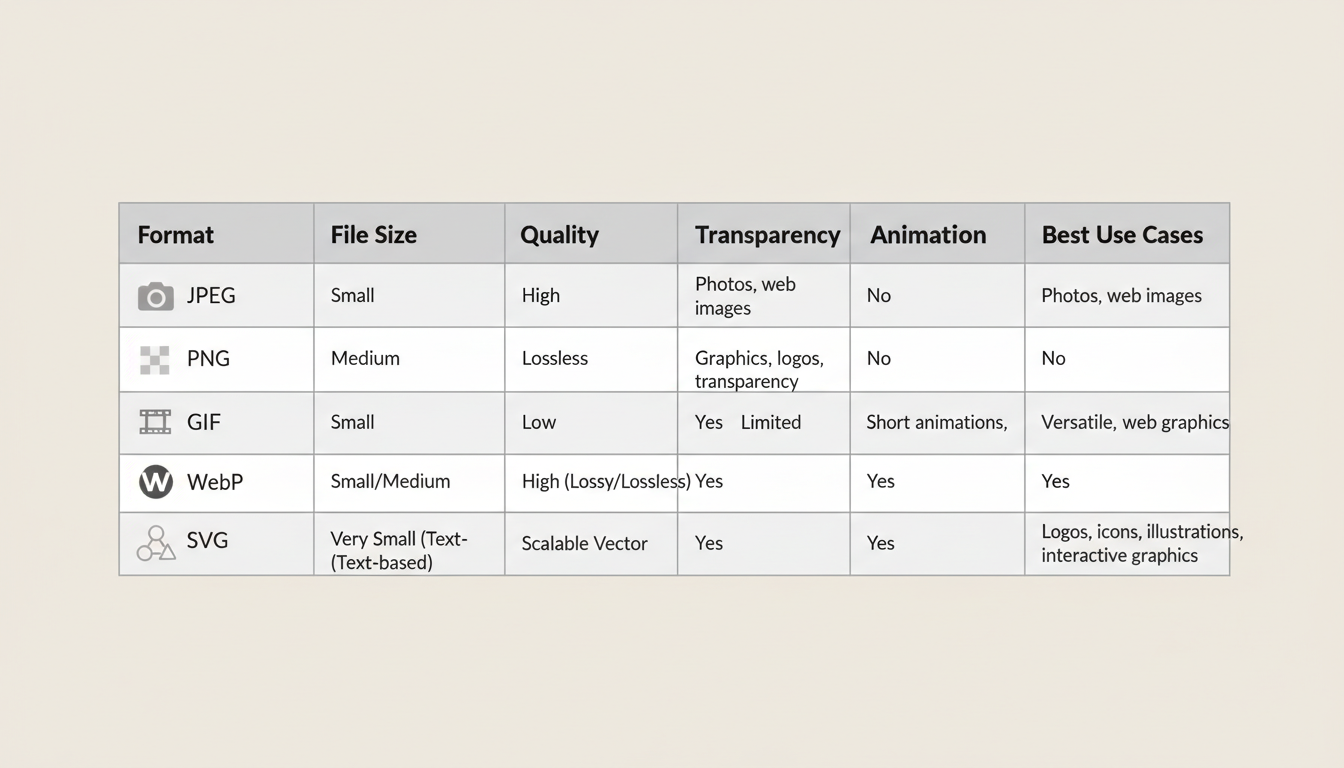
Comparison Table: Key Features
Let’s compare the formats based on important technical attributes:
Visual Quality: JPEG vs PNG
One of the most common decisions is choosing between JPEG and PNG. Here’s a side-by-side comparison:

JPEG uses lossy compression, which reduces file size but sacrifices quality—ideal for photos. PNG uses lossless compression, preserving every detail and supporting transparency—perfect for logos and graphics.
When to Use Which Format?
- JPEG: Best for photographs and complex images where small file size is important. Avoid for text-heavy or transparent graphics.
- PNG: Ideal for graphics, logos, screenshots, and images requiring transparency. Larger file size than JPEG.
- GIF: Use for simple animations with limited colors. Not suitable for photos or high-quality video.
- WebP: A modern format offering both lossy and lossless compression with smaller files than JPEG/PNG. Great for web performance.
- SVG: Vector format for logos, icons, and illustrations. Scales infinitely without quality loss. Perfect for responsive web design.
Conclusion
Understanding image formats helps you balance quality and performance. Use JPEG for photos, PNG for crisp graphics, GIF for animations, WebP for modern web efficiency, and SVG for scalable vector art. As web standards evolve, WebP and SVG are becoming increasingly important for fast, responsive websites.
Now that you know the differences, you can choose the right format for every project!
